Introduction
Modern production plants operate in a dynamic environment where every minute of downtime, every unused machine, and every drop in efficiency translates directly into financial losses. That is why intelligent alert systems, which monitor key performance indicators and respond in real time to any deviations from established norms, are becoming an essential element of modern production management systems.
Alerts are automatic notifications generated by the production system in response to specific events or indicator values that exceed set thresholds. They can relate to various areas – from machine downtime, through quality decline, to deviations in process parameters – for example, the temperature read from sensors. Their task is to instantly inform the relevant people (e.g., operators, shift leaders, maintenance department, or managers) about situations requiring immediate response.
Prometheus, an advanced monitoring tool responsible for the ongoing collection of production metrics, plays a key role in our system's intelligent notification module. These metrics form the basis for defining flexible alerting rules. Thanks to Prometheus, it is possible to create precise alert thresholds, which, when exceeded, automatically trigger a system response – sending notifications to the appropriate people in the organizational structure. The integration of Prometheus with our system enables effective response to critical events before they lead to serious consequences.
Benefits of implementing an alert system
- Quick response to problems
Automatic notifications allow you to identify the source of the problem in real time, which reduces response time and limits the effects of failures or performance drops. - Increased process transparency
Alerts support ongoing production monitoring and ensure transparency – managers can easily monitor the situation on the production floor, even remotely. - Reduction of downtime and losses
Notifying you of potential deviations before they reach a critical level allows for preventive action, which significantly reduces downtime. - Support for data-driven decision making
The alert system collects and archives data on exceeded KPI thresholds, enabling trend analysis and systemic changes based on reliable data. - Increased team accountability and engagement
Clear messages about problems assigned to specific roles help build a culture of accountability and rapid response.
The implementation of smart alerts in a production management system is not just a matter of automating responses to irregularities—it is the foundation of a modern, predictable, and flexible production process. Thanks to them, it is possible not only to respond quickly to problems, but also to detect them early and eliminate their causes. Ultimately, alerts become an invaluable tool that supports a culture of continuous improvement, increasing efficiency, safety, and quality of work at every stage of production.
1. Alerting principle
- The alerting principle is a rule that determines when and how the system should generate alerts in response to specific events.
To use alerts, your account must be configured with the external Prometheus system. To do this, please contact the AndonCloud development team.
The alerting principle in the AndonCloud system is created by selecting the "Escalation" tab and the "Alerting Principles" option.
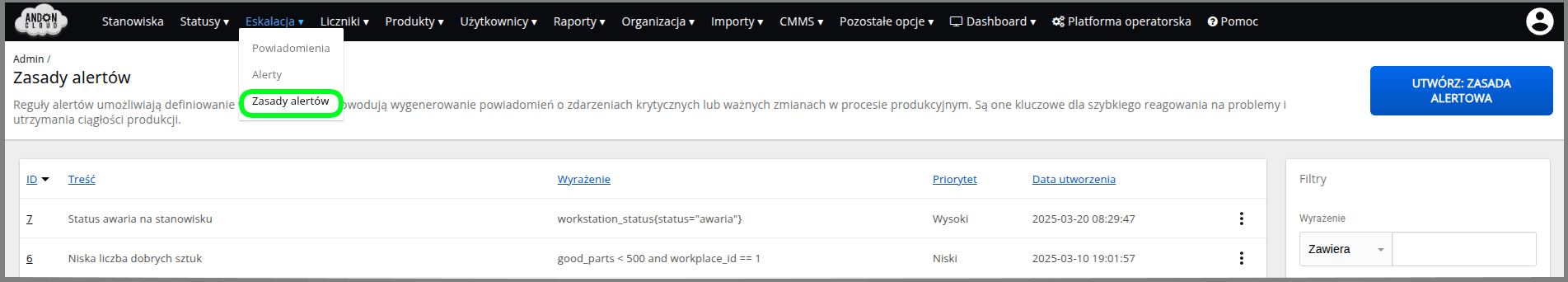
Then, in the upper right corner, select the option: "Create: Alert Rule."
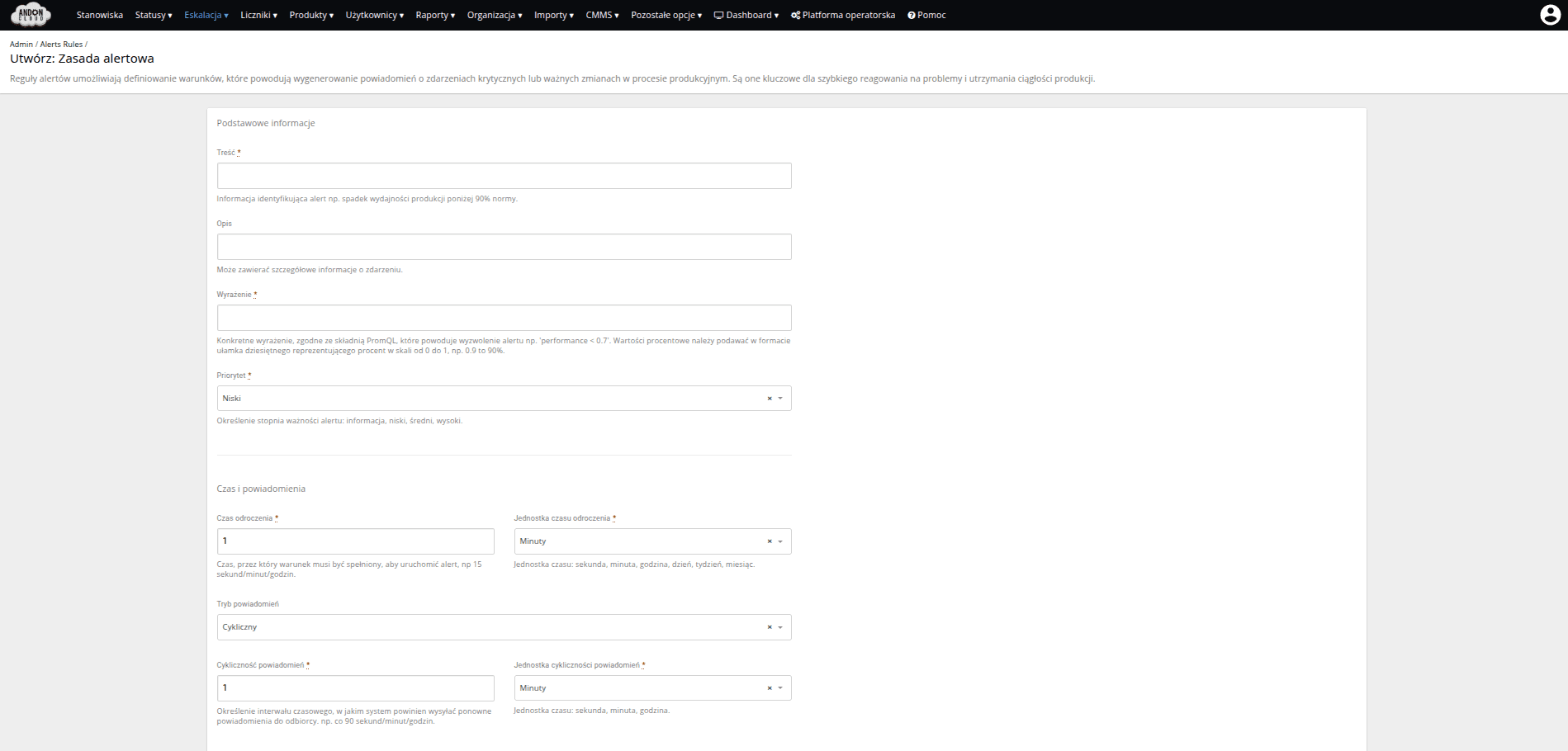
The first field in the form, "Content," is mandatory. It should contain information identifying the alert, e.g., "Production efficiency below 90% of the norm."
The second field, "Description," is optional and can be used to provide detailed information about the event.
To complete the third field, "Expression," use the Prometheus query language, PromQL (Prometheus Query Language). You can learn the PromQL syntax on your own or with the help of the AndonCloud team. For your convenience, we have prepared several suggestions for expressions most commonly used in generating alerts. Examples of expressions can be found in the attachment.
In the next field, "Priority," specify the importance of the alert. The next fields concern the delay time and the frequency of notifications. Specify the time and time unit (seconds, minutes, hours) in these fields. In the last two fields, you can specify the recipients of the alerts. One of the two fields must be filled in for the form to be saved.
For example, below I have described an alert rule that makes it easy to generate an alert. In the first field, "Content," please provide information identifying the alert. In our case, it could be: "Too many defective products." In the "Expression" field, please enter the value: "bad_parts>20."
If you do not specify which workplace the alert should apply to, the system will check every workplace created in the system. To add a workplace, save the expression in the form: "bad_parts>20 and {workplace_id=1}". The system will then check the workplace with Id = 1.
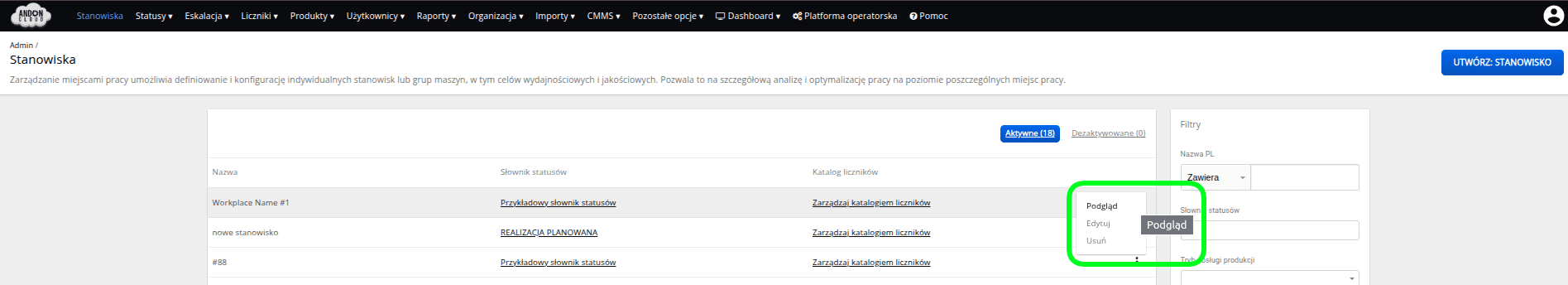
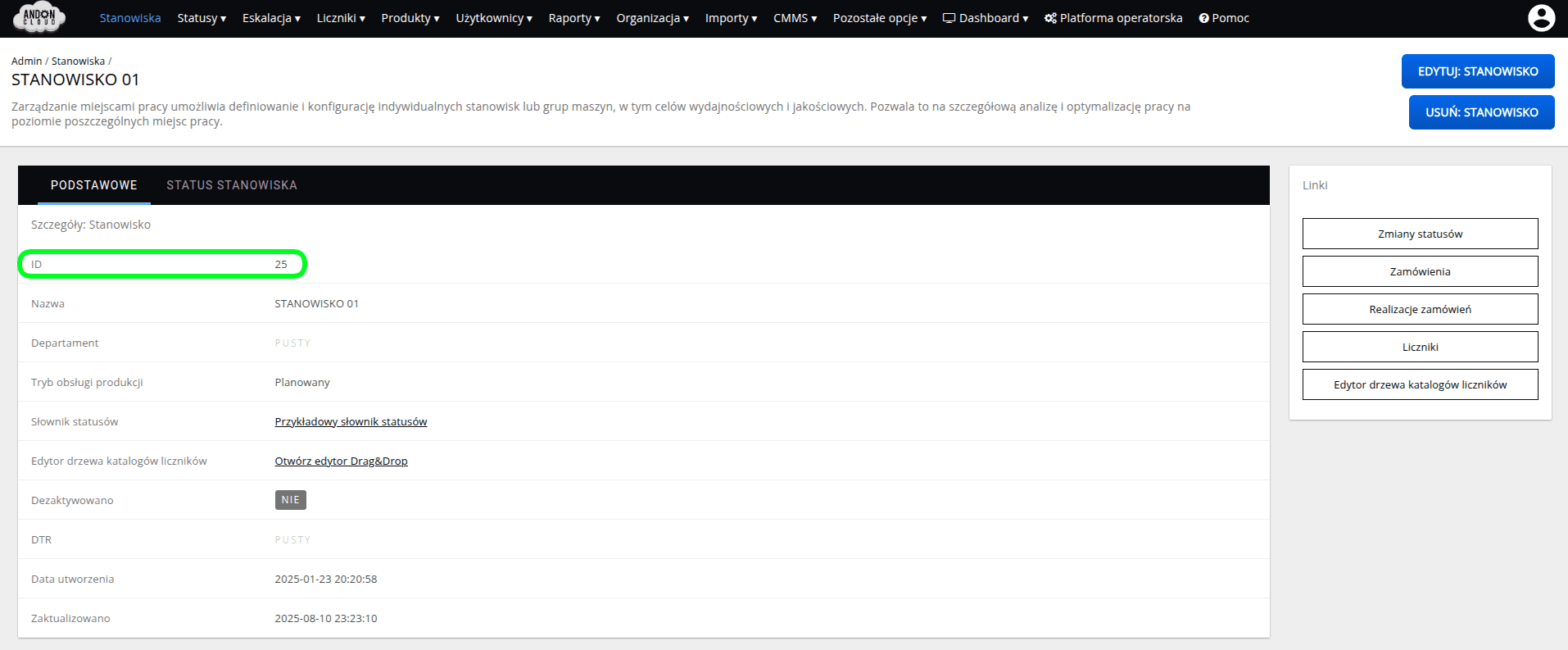
You can check the "ID" of the workplace by selecting the "Workplaces" tab. Select a workplace from the list and click "Preview" in the menu on the right side of the row, marked with three dots.
In the "Priority" field, as I mentioned earlier, you set the importance level of the alert.
Next, in the "Delay time" field, you specify the time that must elapse before the alert is triggered. For example, if you set the time to 30 minutes, this means that if 20 defects are added within the first 30 minutes of operation, the system will generate an alert.
The next field is related to the previous one, namely, when setting the amount of time, you must also set the unit of time. The "Notification frequency" field must be filled in so that the system repeats notifications at the frequency you specify.
Here, too, you set not only the value but also the time unit.
The last two fields are used to specify the recipients of notifications. You can send a notification to a specific person or to all users assigned to a given role. After filling in all the fields, please confirm the form by clicking on the option: CREATE:ALERT RULE
After creating an alert rule, an event must occur that will trigger the creation of an alert and then send notifications to the specified recipients. In our case, the expression describes a situation in which, within 30 minutes of work at the station, the operator will add 20 defects to the meter calculator. So now please log in to the operator panel for any workstation, or if you have specified a workstation ID, log in to the appropriate workstation. Then please start processing the order and within the first few minutes of work add a defect value >20. After 30 minutes, which were specified in the alert rule, the system should generate an alert. (The alert will be displayed in the alert list in the "Escalation" tab in the "Alerts" option.
You have indicated the recipients of the alerts in the form. Now you need to specify how notifications will be sent to individual users. In the AndonCloud system, you can specify, among other things, the communication channel (whether it should be email, SMS, or voice notification). All issues related to "Notifications" are described in the manual: Roles, permissions, and notifications in the AndonCloud system.
2. Alerts
Alerts are used to inform users about important events in the system that require attention or intervention. An alert can be linked to specific rules and configured to reach the appropriate people or groups, ensuring a quick response to potential problems.
Alerts are generated when the conditions described in the alert rule are met. Below is an example of an alert rule and the alert generated.
Alert rule:
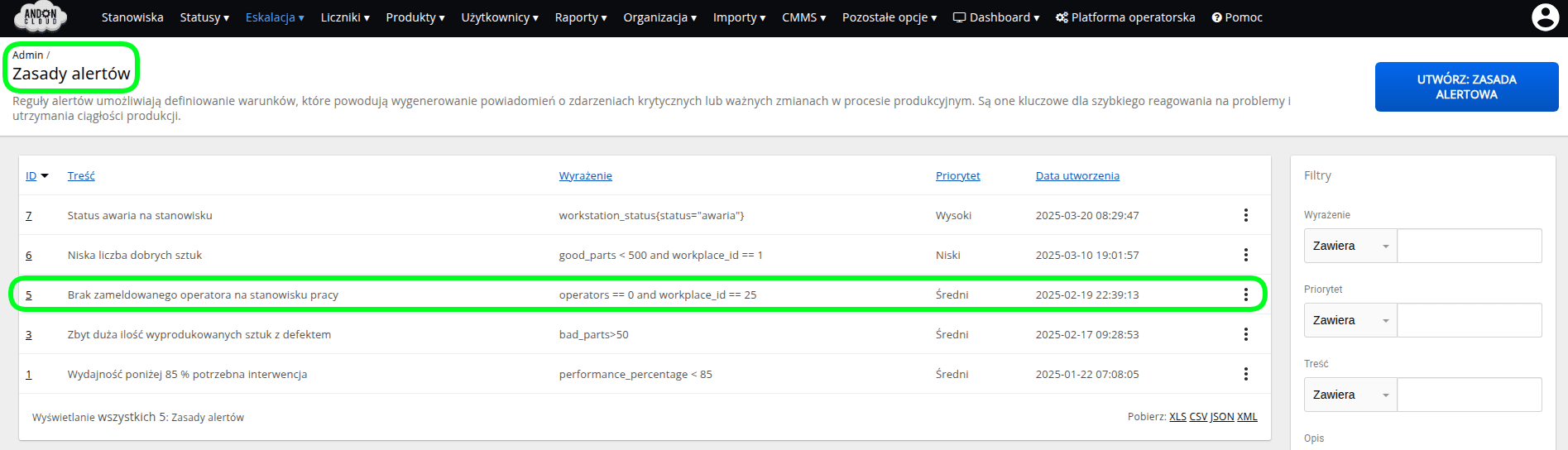
Alert in the Prometheus system
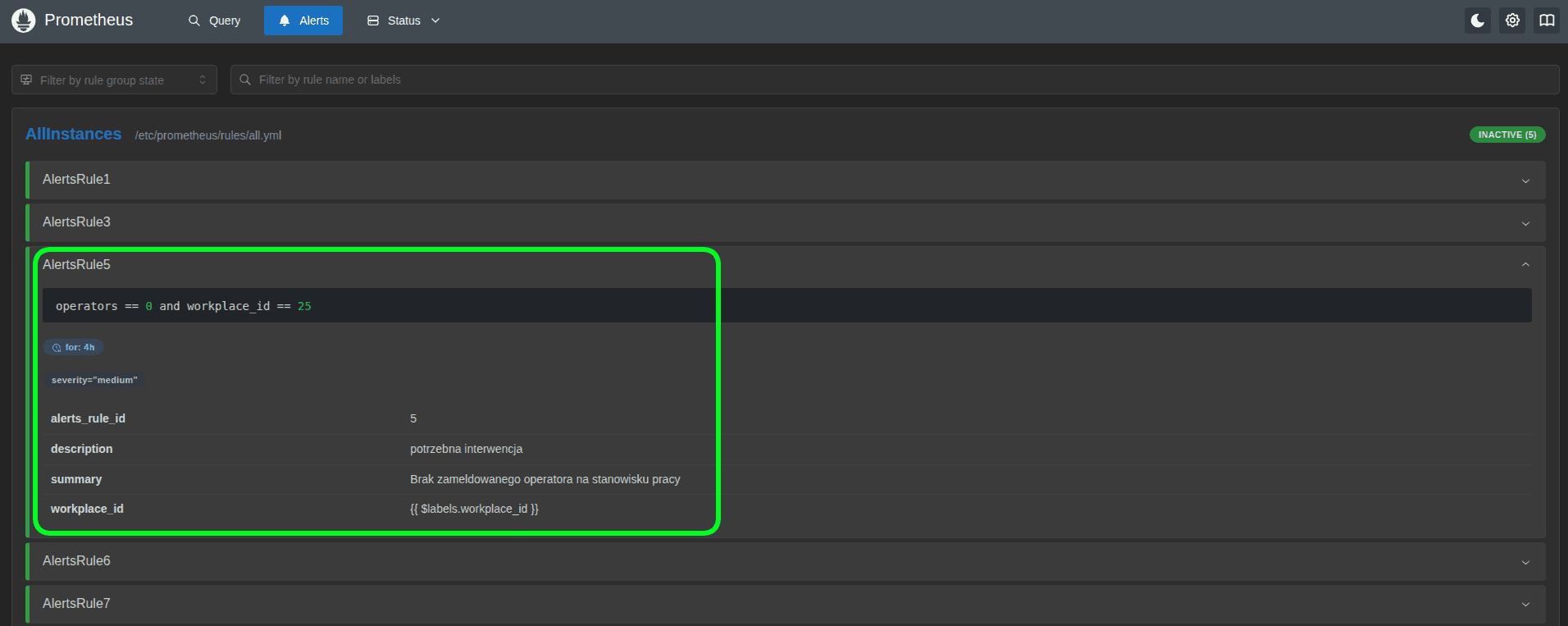
Alert in the AndonCloud system
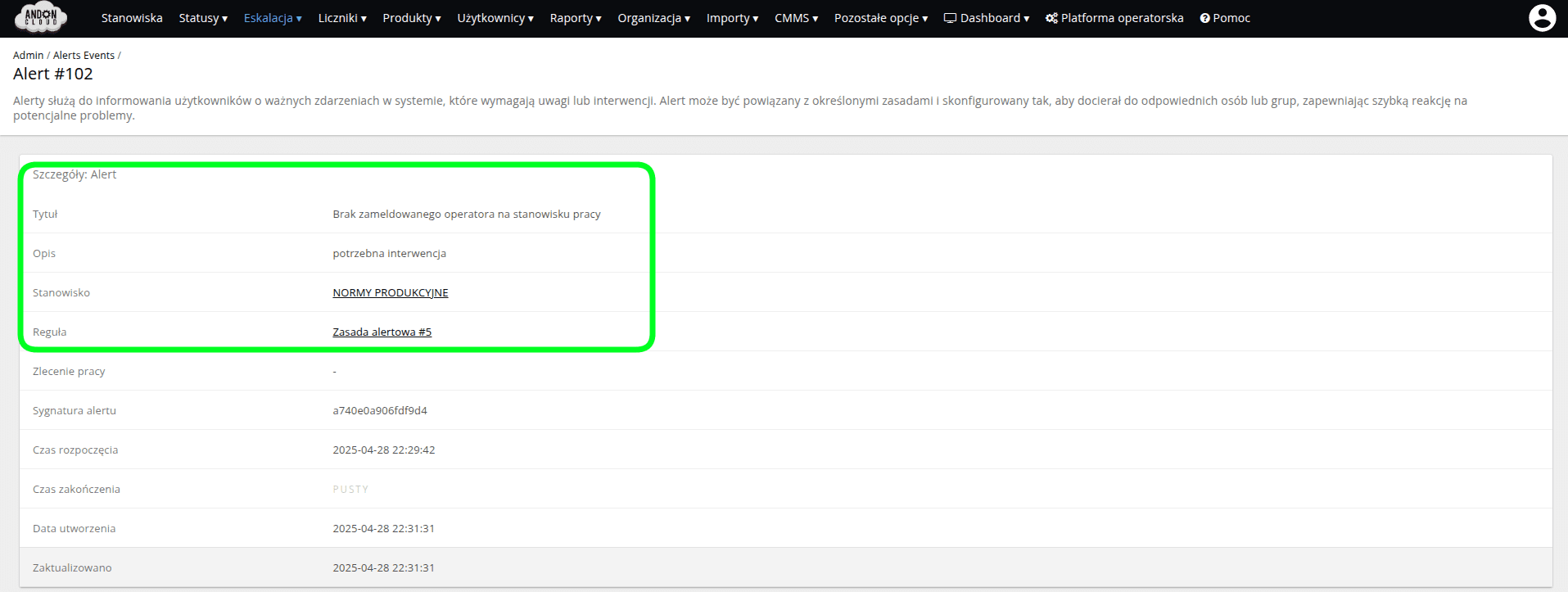
After creating an alert, the system automatically displays a list of active alerts for each workstation.
All ongoing (active) alerts are located in the "Active" tab.
Once the issue related to a given alert has been resolved, the system automatically moves the alert to the "Completed" tab.
Additionally, when a new alert is created, the system sends a notification to all users and roles associated with the alert rule, according to its configuration.
3. Appendix
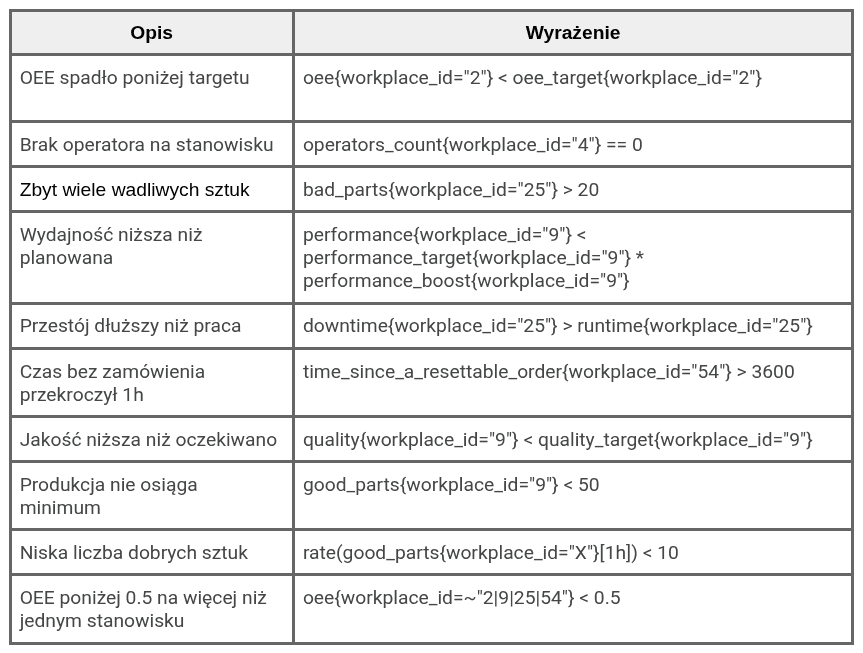
3.1 List of basic labels available for creating expressions
Below is a set of basic labels that can be used when creating expressions in the system.
These labels enable dynamic reference to data associated with specific system elements, such as workstations, machines, or operators.
- ideal_parts_for_runtime{workplace_id="<id>"}
- total_parts{workplace_id="<id>"}
- bad_parts{workplace_id="<id>"}
- good_parts{workplace_id="<id>"}
- availability_target{workplace_id="<id>"}
- performance_target{workplace_id="<id>"}
- quality_target{workplace_id="<id>"}
- oee_target{workplace_id="<id>"}
- availability_boost{workplace_id="<id>"}
- performance_boost{workplace_id="<id>"}
- quality_boost{workplace_id="<id>"}
- oee_boost{workplace_id="<id>"}
- operators_count{workplace_id="<id>"}
- downtime{workplace_id="<id>"}
- runtime{workplace_id="<id>"}
- total_availability{workplace_id="<id>"}
- quality{workplace_id="<id>"}
- availability{workplace_id="<id>"}
- performance{workplace_id="<id>"}
- oee{workplace_id="<id>"}
- time_since_a_resettable_order{workplace_id="<id>"}
NOTE!
Expressions can be created in two ways; for readability, we recommend the first method.
bad_parts{workplace_id="20"} > 20
bad_parts > 20 and {workplace_id="20"}
3.2 Identifying position in expressions
When creating expressions in the system, a specific position can be identified in several ways, depending on the available data or user preferences.
Available labels identifying the position:

The expression will be as follows:
bad_parts{workplace_id="20"}
bad_parts{workplace_name_pl="Name PL"}
bad_parts{workplace_name_en="Name EN"}
The "=~" operator allows you to specify multiple positions at once using regular expressions.
bad_parts{workplace_id=~"20|30|40"} > 20
In the above example, the expression applies to workplaces with IDs 20, 30, and 40, and the additional condition > 20 specifies the threshold value for the alert.
List of sample alert expressions:
3.3 Frequently asked questions
1. What are the typical uses of alert rules?
Alert rules can be used to monitor various production indicators, such as:
Performance falling below a specified threshold,
Exceeding the acceptable downtime,
Incorrect machine parameter values,
No response to previously sent alerts,
Monitoring system failure.
2. Can an existing alert rule be edited?
Yes, once an alert rule has been created, it can be edited by changing the conditions, priority, recipient list, or notification frequency.
3. What are the possible notification channels?
The system can send notifications via:
SMS notifications
Email notifications
VMS voice notifications
4. Can an alert be set for multiple workstations at the same time?
An alert rule can be configured to cover one or more production workstations by selecting the appropriate parameters in the conditional expression.
5. Who can receive alerts?
Alerts can be assigned to individual users or to role groups existing in the system, e.g.:
Operators,
Maintenance technicians,
Production managers,
System administrators.
6. Can I configure a delay for sending alerts?
Yes, you can set the duration of the condition before the alert is generated. This allows you to avoid false alarms caused by temporary parameter changes.
7. How can I check the alert history?
All saved alerts can be viewed in the system using the reports or alert history section. It is possible to filter the results by date, status, or related alert rule.
8. How does alert repetition work?
If the problem is not resolved, the system can repeat the alert at a set frequency.
9. What are the most common mistakes when configuring alert rules?
Setting the alert threshold too low, which leads to an excess of notifications.
Inappropriately selected notification frequency, resulting in spamming users.
No alert recipients assigned, so no one receives notifications.
Incorrectly defined conditional expression that does not correspond to the actual production situation.
10. Can alerts have different levels of criticality?
Yes, each alert rule can be assigned a priority, e.g.
Low – informational notification,
Medium – requires attention but not immediate response,
High – critical issue requiring urgent intervention
Summary
The alert module in the AndonCloud system supports ongoing monitoring of production processes, facilitating quick responses to changes.
Thanks to flexible alert rules based on data from the Prometheus system, users can quickly respond to deviations from the norm and detect potential causes of downtime in advance.
Proper configuration of alert rules enables:
- real-time monitoring of key production indicators,
- automatic notification of relevant personnel about problems,
- contributing to faster response times and reducing the number of unplanned downtimes,
- supporting a culture of responsibility and process improvement.
It is recommended to regularly review alert rules in the system administration panel to adjust them to current conditions and production goals.
If you have any doubts about the configuration or need to create advanced rules, please contact the AndonCloud support team.